The gender employment gap – an issue that affects us all
In his recent State of the Union address, European Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker laid out his vision for the EU over the next 12 months. There was no shirking of responsibility; Europe faces difficult challenges, and the EU Institutions, as well as the Member States, must deliver for EU citizens and those that call Europe home.
The State of the Union address acknowledged the particular challenges posed by Brexit and the developing migrant crisis but was not defined by these issues. The need to build a Europe that protects and empowers its citizens was at the very core of the address, focusing on the common values that we share in Europe, what unites a farmer in Lithuania with a single mother in Zagreb.
European Commission: State of the Union 2016
One such common value is that of equal participation in society and equality of opportunity; that we should have the same possibility to improve our lives and make progress in our careers regardless of our gender, ethnicity, religion, sexual orientation, whether we have a disability or where we come from in the Union. And yet, Eurofound’s recent research has highlighted that issues such as the polarisation and the segmentation of European labour markets continue to persist. Our latest report The gender employment gap: Challenges and solutions shows that the gap between male and female participation in the labour market remains wide. Despite a notable increase in women’s labour market participation in recent years, the female employment rate is still more than 10 percentage points lower than the male rate. This is in addition to research showing that women are more likely to work part-time in Europe, and that a clear gender segregation of occupations and workplaces persists, as shown in the figures of the European Working Conditions Survey.
There are clear ethical and political implications resulting from this inequity. There is also a significant financial cost to Europe. The gender employment gap is equivalent to an overall loss to the economy estimated at around €370 billion, or 2.8% of the EU’s annual GDP; comprising the forgone earnings and missed welfare contributions of non-working women to society, as well as the public finance cost, comprising individual welfare transfers and social benefits. This figure does not include the contribution in caring and other domestic activities made by women outside the labour market, which have not been properly estimated at EU level. It could be argued that the cost of a lower participation of women would be, at least partially, offset with the savings for (mostly care) services not provided by the Governments. At the end of the day, this reflects the broader question about the model we want for society; one based on the division of tasks based on gender, or one based on equal opportunities and equal participation aligned with the EU values.
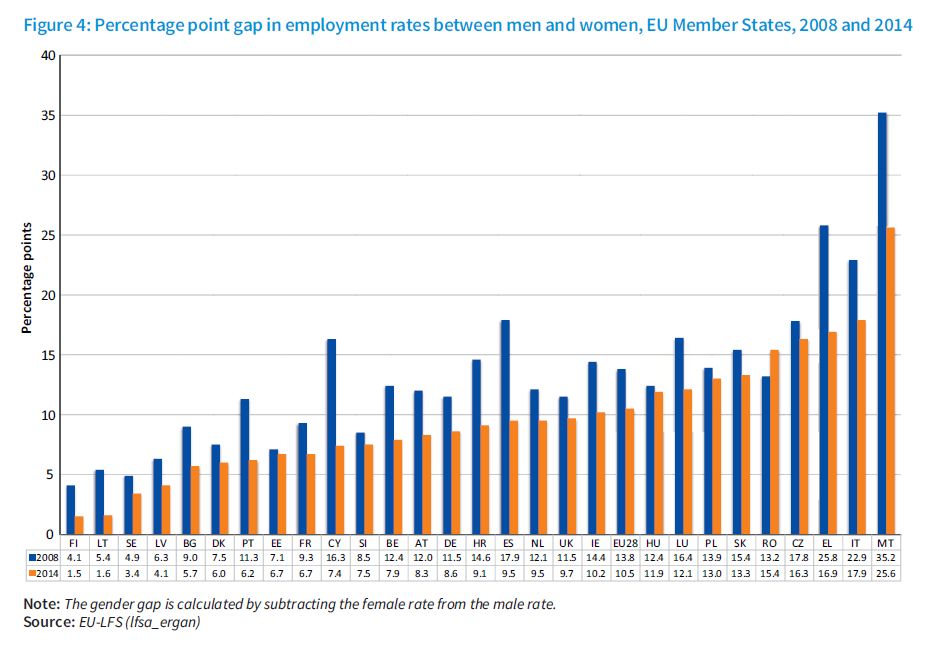
Examining the recent evolution of the labour market, the good news is that there has been a convergence between female and male employment rates since 2008. However, this has been largely driven by a relative worsening of the male employment rate and the decline of previously male-dominated industries such as construction. The decline in employment in these industries, partly influenced by the process of digitalisation and automation, has lessened the gap from a statistical point of view. In any case, examining scenarios for the coming years, it is clear that the EU will not meet its target on female participation. If progress were to continue at this rate it could take up to 30 years in many Member States to achieve EU targets.
Empowerment can be driven through a myriad of social and economic policies, as well as business practices that can impact directly, and positively, on the gender employment gap. The report summarises a number of these, including the availability and affordability of childcare, the accessibility of, and social practices relating to, parental and adult care leave, as well as the provision of flexible working arrangements. In particular, in many Member States, an integrated approach to family policies would drive up the labour market participation rate of women by 14% during the next 30 years.
The findings show that Member States that have been successful in reducing the gender employment gap in Europe have implemented several of these policies to reduce barriers to employment. At the same time, they have emphasised the importance of employers recognising employees’ need to reconcile care responsibilities with work more generally – an approach from which the workforce as a whole, women and men, as well as employers, can benefit.
The gender employment gap is not a new issue; gender equality was a significant challenge when it was established as a priority with the Directive on equal treatment between men and women in employment 40 years ago, and it has been always part of the EU strategy. But this does not make it any less pressing, to be put on the back-burner until after Brexit or until the migrant crisis has been dealt with. Nor is the gender employment gap a ‘women’s issue’ or an issue for one European Parliament or national parliament committee in isolation. It is an issue of importance for all stakeholders, from SMEs to the European Commission, because, as President Juncker said ‘solidarity is the glue that keeps our Union together.’
More reading:
World Economic Forum: Global Gender Gap Report
Related links
Publication: The gender employment gap: Challenges and solutions
Publication: Sixth European Working Conditions Survey – Overview report
Author
Related content
11 October 2016
The gender employment gap: Challenges and solutions
Women’s labour market participation in the European Union has increased over recent decades, passing 70% in 2014. In that year, women comprised almost 46% of the active EU labour market population. Nevertheless, women’s employment and participation rates are still lower than those of men in almost all Member States. Fostering higher participation of women is crucial to meet the Europe 2020 target to achieve an overall employment rate of at least 75% by 2020. This report explores the main characteristics and consequences of gender gaps in labour market participation. It finds that the total cost of a lower female employment rate was €370 billion in 2013, corresponding to 2.8% of EU GDP. The report also examines policies and measures aimed at fostering female labour market participation, which could be central to closing gender gaps. An annex, published separately, contains details of policy measures to support the labour market participation of women.
17 November 2016
Sixth European Working Conditions Survey – Overview report
8 March 2017
Reducing Europe’s gender employment gap
28 September 2016
